| Market Cap: ₪816M TTM revenue: ₪191.6M YOY return: +23.29% |
CEO: Noam Segal Cumulative pay: ₪6M (est) Shareholder value created: -₪342.2M |
Forecast effort: F Forecast accuracy: F |
 |
mageSat International (ISI) is a once-profitable Israeli “old-space” provider of Earth observation services, offering optical and radar satellites. ISI stock trades on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange. ISI specializes in advanced imagery AI and data analytics leveraging its imagery. All but one of ISI’s six largest customers are governments. ISI traditionally operated large, high-spec satellites up to 400 kg, competing with Maxar, Airbus, and Satrec. ISI recently crossed over, becoming the only “old-space” provider also offering smaller “new-space”-sized satellites, competing with BlackSky, Planet Labs, and Satellogic. Management failed to hit its business targets post-IPO. Both profits and ISI’s stock price are down. In 2024, ISI closed two new large contracts, suggesting significant revenue growth in 2025. However this has yet to develop and ISI’s backlog remains flat.
2 Minute Version
- Imagesat International (ISI) is an old space satellite imagery provider. Founded in 1997, ISI operates satellites comparable in size and spec to Maxar, Airbus, and Satrec. ISI’s main customers are international governments unhostile to Israel.
- ISI does not manufacture its own satellites. ISI purchase satellites from related party (shareholder) Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI), and more recently from Terran Orbital (United States) and ST Engineering (Singapore). This lack of vertical integration makes ISI an outlier among satellite imagery providers.
- ISI originally planned to go public on the U.S. Nasdaq with a $500m market cap in 2006. Infighting over targeting Venezuelan sales, and Hugo Chávez making a potential $150m investment resulted in litigation. The Nasdaq IPO later collapsed.
- Sixteen years later ISI went public on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange in February 2022 with a valuation of approximately $370 million.
- ISI’s satellites are among the highest spec commercial imagery satellites in the world. Its EROS NG constellation in comprised of two SAR and four optical imagery satellites with resolution up to 30 cm.
- ISI operated profitably leading up to its IPO with revenue growing with CAGR of 10%. However, growing debt remains concerning. Profits dipped in 2022 before rebounding in 2023, but remain below 2019-2021 levels. And debt grew to approximately nine-times 2023 profit.
- Five customers comprise 85% of ISI’s sales. Three of these five customers generally show declining YoY sales, while two show gains. (original research)
- ISI’s backlog peaked in 2Q 2022 and since is down approximately 20%. In September 2024, ISI announced a $54 million, three-year contract with an unnamed international defense customer. This single contract equates to $18.2m in yearly revenue, a value more than 40% of ISI’s total revenue in 2023.
- The same month, ISI announced another contract to provide two “new-space” class Runner satellites to an Asian customer. Based on costs ISI reported for its first Runner satellite, this contract likely values at least $30m. (original research and analysis below)

Examining Financial Disclosures
From 2018 to 2024, revenue impressively grew from $27 to $58 million. However ImageSat posted net loss in 2024 and remains unable to make a dent in its debt, currently standing at $31.4m. ISI’s debt stems from loan(s) from Israel Aircraft Industries (IAI), an ISI shareholder and manufacturer of ISI’s EROS line satellites. ISI’s 1Q 2024 filing advised it anticipated new sales contracts providing sufficient cashflows to alleviate ISI from needing outside money to satisfy debt obligations. The aforementioned $54.5m and Runner contracts ISI announced in September 2024 so far gives credence to management’s statement. And debt has subsided approximately 25% since 2023.
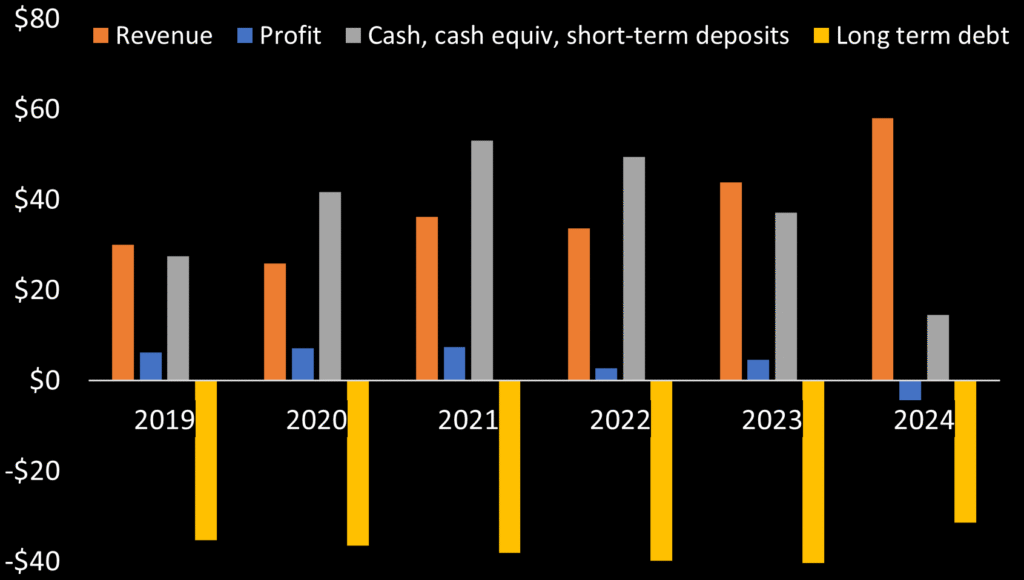
On quarterly basis, ISI revenue has trended upward but Q1 2025 saw significant decline. ISI writes that revenue was pushed out to later quarters in 2025. And ImageSat which was net profitable each year from 2019 to 2023, finds itself in a rut. Since 1Q 2025 ISI has posted five straight quarters of net loss with Q1 2025’s loss amount greater than revenue.

ISI’s most significant contract is with Chile. In 2019 Chile requested bids from Maxar, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, Ball Aerospace, and likely others. ISI outbid all to win the deal in May 2021. ISI clearly competes on cost well against old-space. Under the contract, ISI provides Chile nine satellites, ground systems, imagery from ISI’s existing constellation, and data/analytical services for $109.9m. In August 2021, Chile paid ISI an $24.6m advance, which at the time was not recognized as revenue.
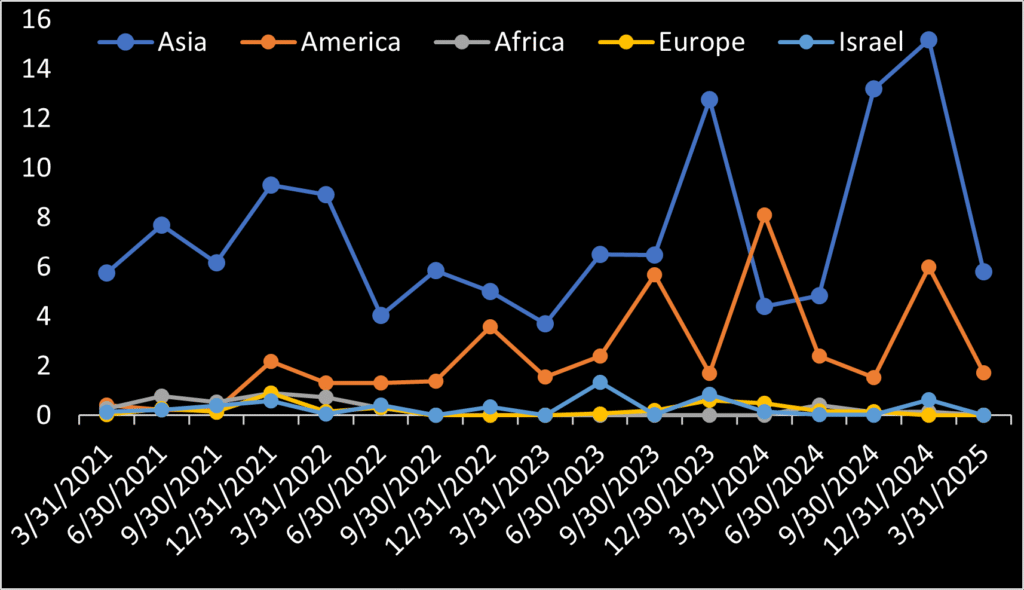
ISI discloses revenue by region. Plotting data from its various financial reports reveals two things. First, Asian customer have provided the majority of ISI revenue until recently when American (Chile) revenue took over. Secondly, domestic sales to Israel remain almost negligible. Blacksky apparently succeeded in signing Israel as a government customer. Plenty of upside should exist should ISI establish sales to its home government.
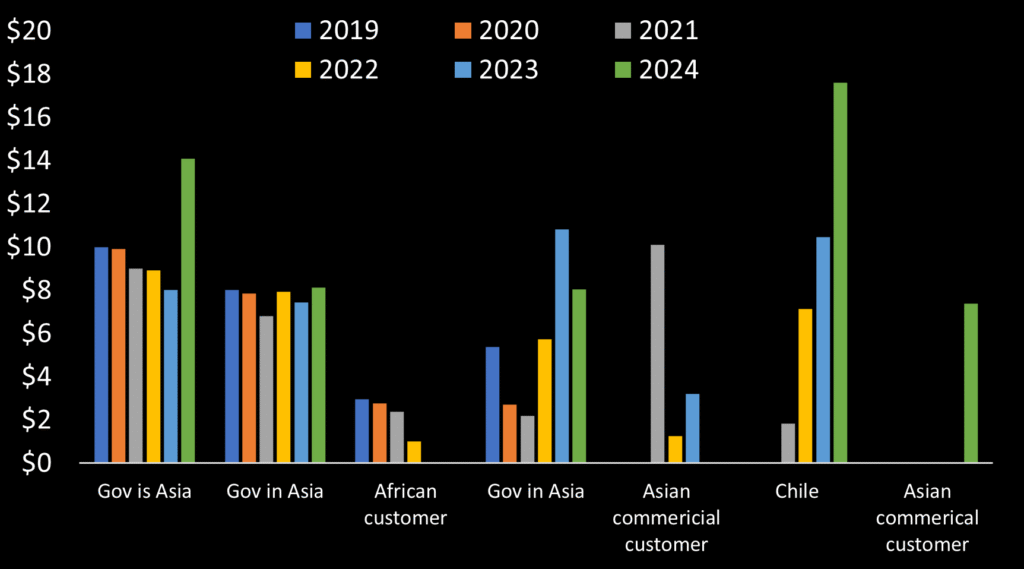
ISI identifies no other major customers by name. Sales are reported by region and disaggregated by unnamed customer identified as Customer A, Customer B, etc. However, comparing customer sales with regional revenue allows, by process of elimination, identification of each customer’s region. Of five remaining customers, three show a general trend of declining revenues YoY. An African customer that apparently is no longer, showed a similar trend through 2022.
Backlog Reporting (“ISI, what are you doing?”)
Finally, the last interesting metric ISI reports is backlog. Total backlog has been relatively flat for 3 years.
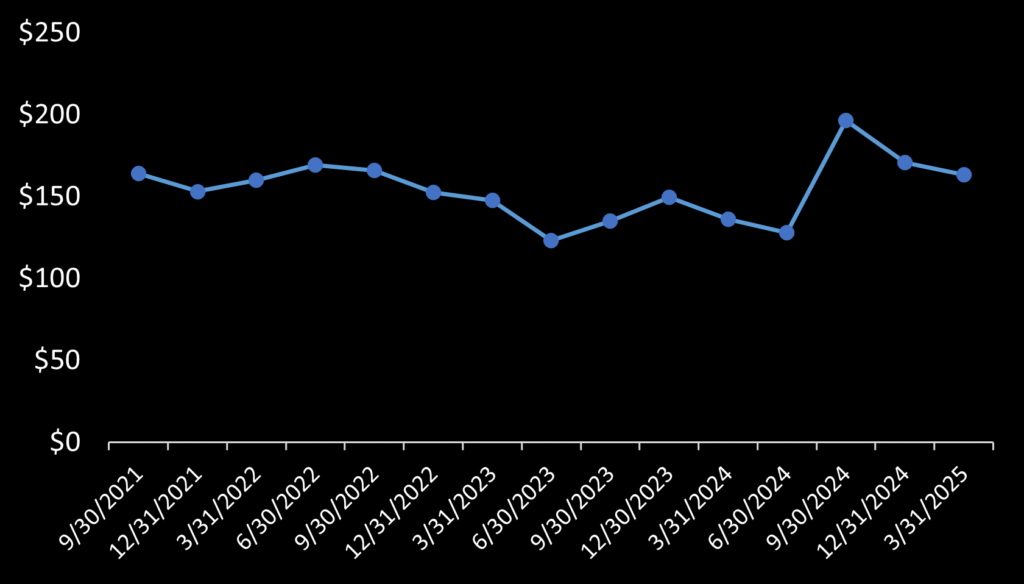
However close examination reveals something off about backlog reporting. ISI announced in January 2024 a 5-year imagery contract worth $37.5m. In 1Q 2024, ISI posted $13.2m in revenue. Assuming all $13.2m in revenue was accounted for by ISI’s reported backlog as of December 31, 2023, backlog that quarter should have grown $24.3m. Instead ISI’s posted that backlog decreased by $13.4m, an amount even greater than the quarter’s total revenue. Something is really odd here. (🚩) It seems either ISI is fiddling with its backlog reporting, or customers are cancelling orders and ISI is mum about it to shareholders.
This is not the first time something strange can been seen in ISI’s reported backlog. ISI reported in its January 31, 2022 pre-IPO investor presentation that backlog stood at $171m as of December 31, 2021. ISI claimed recently executing a contract that had “retroactive effect for 2021.” However, after its IPO, ISI reported its backlog as of December 31, 2021 was $153m – a value $18m lower than what it reported pre-IPO.
One way to interpret this is that ISI did not want to report to investors its backlog was declining before completing its IPO. On January 17, 2022 when ISI announced its IPO, it reported backlog as of September 30, 2021 was $163m. If ISI reported backlog as of December 31, 2021 slipped to $153m prior to its IPO, this would create mild investor concern. ISI two weeks later put a chart in its investor presentation captioned “growing revenue backlog”. This chart showed backlog grew $7m between 3Q and 4Q 2021.
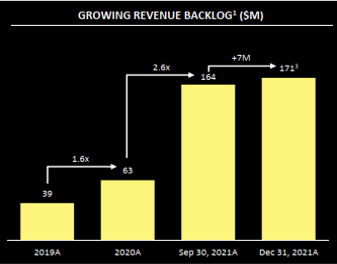
After ISI successfully completed its IPO, they stopped reporting $171m as the 2021 end-of-year backlog, replacing it with $153m.
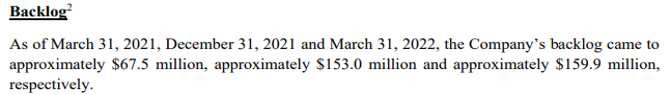
Back dating contracts to show backlog growth is not necessary. Prospective investors don’t want to see this. The numbers just are what they are. ISI would better serve shareholders through increased transparency.
Runner Satellite
Imagesat with competitors Airbus, Maxar, and Satrec traditionally operated high-res satellites weighing 100s of kilograms. New space contenders Planet Labs, Blacksky, and Satellogic (and to some extent Axelspace) utilize a significantly lighter satellite class with only slightly lower resolution. Imagesat is so-far the only old space player to crossover offering earth observation satellites in the new-space class: “Runner.” ISI describes Runner as “a cost-effective and affordable solution”, with 70cm resolution at 86 kg. This is comparable to Blacksky Block-2 and Gen-3, Planet Lab’s Skysat and Pelican, and Satellogic’s satellite lines.
So far ISI has delivered one Runner which Chile uses. Chile will receive two more Runners under its existing contract. And another unknown Asian customer recently ordered two more “Runners”.
ISI’s 2023 annual report revealed ISI paid $7.13 million to Tyvak/Terran Orbital for the first Runner, with $250k balance still due. ISI paid an additional $6.6m for this satellite to other parties. Thus the total cost to ISI for Runner-1 was about $14m. This price is clearly higher than new-space competitors offering satellites in the same ~70cm resolution spec class. However one feature setting Runner apart is direct command access by customers. Customers wishing to autonomously and privately task imagery, can do so with Runner. Competitor satellites requiring tasking through the operator’s system, so tasked imagery is not completely confidential.
Management guidance scorecard
ISI provided a few financial forecasts pre-IPO. Twice in January 2022, management forecasted $102-134m in 2024 revenue on top of EBITDA forecast. ISI appears on track to miss the midpoint of that guidance by 50%!
Post IPO, ISI stopped issuing guidance. The closest found to a projection is management advising in its 1Q 2024 report that ISI near closing some sales contracts. Truth be told, ISI later did just as management guided.
CEO compensation and performance
Noam Segal leads ISI as CEO. Unlike US-listed public companies, Israeli does not require disclose of individual executive compensation. Whereas Noam Segal’s total compensation is unknown, ISI discloses cumulative pay of its five key managers. These managers collectively received $1.8m in compensation in 2019, and $2.2m in 2023. This equates to about $450,000 per. However pay almost certainly is not divided uniformly, and Segal likes receives more than others.
ISI in 2024 disclosed Segal’s salary raised to 90,000 Shekels per month March 2024. The same month ISI also provided Segal 459,640 options, but with with unknown value.
Noam Segal’s performance, as measured by shareholder value created, puts him among the class of space CEO losers. At IPO, ISI entered the market worth 1.15B Shekels. Accounting for the approximate value of new shares at issuance, approximately 345m Shekels of shareholder value ($93m) has been lost under Segal’s watch.
ISI outlook and risk assessment
ISI is no longer profitable but has cut down its debt. ISI’s largest risk lies in potential margin erosion and ISI not debt persistence. Current debt arose from financing existing revenue-generating satellites. If ISI’s margins decline and debt is not repaid, ISI may find itself unable to finance the replacing of its current fleet. This risk does currently not look too high, but the persistent debt and potential margin squeeze is indeed worrisome.
- ISI appears so far immure to the threat of new-space operators Planet/Blacksky/Satellogic. Blacksky generates revenue mostly from U.S. government sales, where ISI does not compete. Planet generates significant revenue from 3U imagery, where ISI also does not compete. So ISI’s sales channels generally are not in conflict.
- But there are customers where ISI and new space firms complete in common (Blacksky’s Indonesia contract for example). But so far ISI does not appear to have experienced any customer poaching. The only possible exception is the African customer ISI lost two years ago. This is the smallest of ISI’s six main customers, but not know if a new-space competitor won this customer or not.
- ISI likely will miss its forecast of $102 to $134m revenue in 2024. However, the two new contracts announced in September 2024 should present ISI with significant 2025 revenue growth.
- The yearly decline in revenue by customer noted above my be evidence of price erosion from competitive pressure. Similar decline in revenue-per-customer may be observed from analyzing Planet Lab’s financial data. If such price decline exists and persists, it will certainly pressure ISI’s margins.
- However, ISI’s proven ability to outcompete old-space satellite operates – ISI’s main competitors – for foreign contracts suggests

ISI has operated profitably for each of the at least past five years. If ISI can maintains current margins, expected revenue growth from announced contracts should lift profits. Thus risk of doubt generating of ISI’s ability to continue is a going concern seems rather low.
What to look from ISI going forward
Aside from the obvious (increasing profitability back to prior levels), look for the following:
- ISI will find access to capital to fund its next satellites more difficult if they carry too much debt. ISI has for five years been treading water. ISI needs to pay down this debt to make room for more debt to fund its next generation of satellites.
- Shareholders should demand business forecasts from ISI. Management undoubtably is happy to continue not providing any. But executive compensation linked to achieving public business goals seems to be a standard practice in corporate governance.
- ISI customer year-on-year spend appears, at least for some customers, to be slightly decreasing. This may be evidence of downward price pressure from abundant competitor imaging supply. If the same customers continue to decrease spend year-on-year, this may be evidence imagery margins are facing pressure.
- Does Blacksky win another contract like its recent $50m Indonesian contract? This was supposed to be ISI’s segment. Blacksky’s Gen-3 satellites are certainly cheaper than ISI’s Runner. (Maybe by a factor of 2x?!) So Blacksky winning another deal to provide autonomous satellites to a nation-state should give concern about ISI’s future success with Runner.
Recent News
-
ImageSat 2025 1Q results: steep net loss, sales challenges
ImageSat International (TLV: ISI) had a tough 2025 first quarter, posting its largest net quarterly loss since going public three years ago. A quarter-on-quarter drop…
-
Satrec Initiative offering secure tasking with SpaceEye-T
Satrec Initiative (KOSDAQ: 099320) launched its next-generation SpaceEye-T imaging satellite on a Falcon-9 bandwagon launch in March 2025. Previously, Satrec sold imagery via a tasking…
-
Satrec 2025 first quarter financial performance
Satrec Initiative (KOSDAQ: 099320) reported its 2025 Q1 financial performance. Revenue totaled ₩40.0 billion (~$28.3 million), a 17.3% dip from 2024 Q4 but 26.2% more…
-
ImageSat International’s flagship EROS-C3 satellite experiences in orbit anomaly
ImageSat International’s (TLV: ISI) 30 cm ultra-sharp resolution EROS-C3 earth surveillance satellite suffered two anomalies in orbit. Built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), EROS-C3 launched…
-
Global satellite earth imagery market as seen through public company financials
Five satellite earth observation companies trade publicly: Planet Labs (NYSE: PL), Blacksky (NYSE: BKSY), Satellogic (NASDAQ: SATL), Satrec (KOSDAQ: 099320), and ImageSat (TLV: ISI). Yes,…
-
US & Israel use Blacksky and Maxar satellite imagery for Hamas War, not so much Planet Labs or Satrec
More fantastic reporting by Intelligence Online: shortage of Israeli homegrown SAR and optical satellites has provided opportunity for Blacksky and Maxar. Israel’s ImageSat (TLV: ISI)…